When engaging in cross-border trade, particularly for trucking and logistics companies entering Canada, understanding and utilizing the Highway Carrier Code is fundamental. Issued by the Canada Border Services Agency (CBSA), this unique identifier serves as a crucial element in Canada's customs processing system. Here's a closer look at what a Highway Carrier Code is, its importance, history, and its role in streamlining cross-border trade, including PARS barcodes, ACI eManifests, and the steps involved in applying for one.
Definition of a Highway Carrier Code
A Highway Carrier Code is a four-character alphanumeric identifier assigned to highway carriers (trucking companies) that are engaged in the transportation of goods across the Canadian border. This code is essential for carriers because it identifies them in CBSA's system and is mandatory for submitting advance cargo information and eManifest data to the Canadian government.
Without a valid carrier code, carriers will face delays at the border, and their shipments may be held or even refused entry into Canada. The code ensures the carrier complies with customs regulations, allowing for smoother and faster processing of shipments.
The History and Development of the Highway Carrier Code
The requirement for highway carriers to have a specific identification code goes back to the early 1990s when the Canadian government implemented stricter measures to monitor and facilitate cross-border trade. This system was originally designed to enhance border security while reducing the time and paperwork involved in processing shipments.
With the rise in trade volume between Canada and the United States—particularly following the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA)—CBSA saw the need for a more efficient system to track and process the growing number of highway shipments entering Canada. The Highway Carrier Code system was introduced as part of efforts to modernize customs procedures and leverage technology for quicker, more efficient border operations.
The Highway Carrier Code and its Role in Cross-Border Trade
The primary purpose of the Highway Carrier Code is to uniquely identify carriers in CBSA's system for customs and regulatory purposes. However, it also plays several vital roles in the day-to-day operations of cross-border trade:
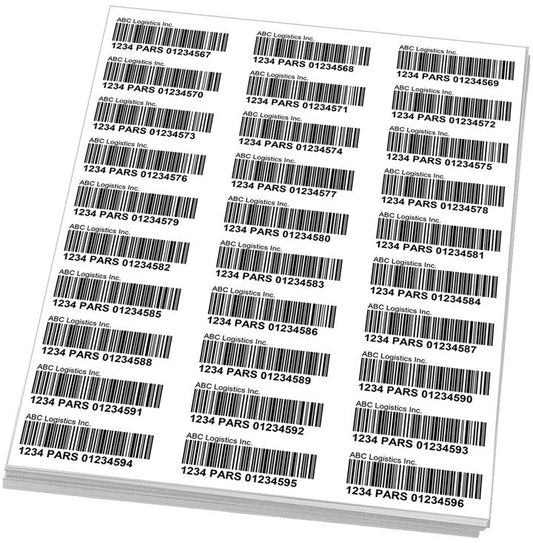
1. PARS Barcode Labels
The Pre-Arrival Review System (PARS) is an important aspect of Canada’s customs processes. Highway carriers must submit paperwork and cargo information in advance to CBSA, allowing the agency to review the details before the shipment arrives at the border. A PARS barcode label is attached to each shipment, which includes the carrier's Highway Carrier Code.
This system significantly reduces wait times at the border, as the goods are pre-approved and can be cleared quickly. Without a valid Highway Carrier Code, the PARS system cannot function, and carriers would face long delays.
2. ACI eManifest
In 2010, CBSA introduced the Advance Commercial Information (ACI) program to enhance trade security and streamline commercial traffic entering Canada. Under this program, highway carriers are required to electronically submit cargo and conveyance information before arriving at the border, which is known as an eManifest.
The ACI eManifest must include the Highway Carrier Code, as it links the electronic submission to the specific carrier and shipment. This allows CBSA to pre-screen cargo for any potential security risks, helping to avoid unnecessary delays or rejections at the border. ACI eManifests are now mandatory for all highway carriers entering Canada, and failing to submit one correctly can lead to fines or other penalties.
Steps to Apply for a Highway Carrier Code
Before a highway carrier can start using a Highway Carrier Code, they must go through several steps to ensure they are in compliance with CBSA regulations. Here's an overview of the process:
1. Business Number (BN) Registration
First, the carrier must register for a Business Number (BN) with the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA). This number is necessary for tax purposes and is required before any application for a Highway Carrier Code can be submitted.
The Business Number consists of 9 digits, and once the carrier has registered with the CRA, they will receive a BN that is required for customs-related transactions.
2. Completion of CBSA’s Application for a Carrier Code
After obtaining a Business Number, the next step is to complete CBSA’s Application for a Carrier Code (Form BSF329-7). This form requires detailed information about the carrier, including:
- Business Name and Address
- Business Number (BN)
- Contact Information
- Description of the Business Operations (e.g., type of goods transported, regions of operation)
- Agreement to abide by CBSA’s rules and regulations for customs and border security.
3. Submit the Application
Once the form is completed, it must be submitted to CBSA for review. The agency will evaluate the application and, once approved, will issue the carrier a unique Highway Carrier Code. The approval process can take a few weeks, so carriers should apply well before they intend to start cross-border operations.
4. Training and Compliance
After receiving the Highway Carrier Code, it’s essential for carriers to ensure that their staff are properly trained on using the code in conjunction with PARS, ACI eManifest, and other customs procedures. Additionally, carriers must stay up-to-date with any changes in CBSA regulations to avoid penalties.
Conclusion
The Highway Carrier Code is a vital part of Canada’s customs and border processing system. Whether it's ensuring pre-approval through the PARS system or submitting ACI eManifests in advance, the code streamlines the cross-border movement of goods and helps CBSA manage the influx of highway shipments more efficiently.
For any highway carrier looking to do business with Canada, obtaining and properly using a Highway Carrier Code is not just a legal requirement but a key component of successful and timely cross-border trade.
Ensuring that your company is set up with the correct code, understanding the history of its development, and familiarizing yourself with the associated systems like PARS and ACI eManifests will allow your business to operate smoothly and effectively in the competitive landscape of cross-border transportation.